Chemistry Notes: Periodic table For 11th, 12th Class (CBSE, ICSE & UP Board) PDF
CBSE, UP and ICSE Board Chemistry Notes and Periodic table. Class 11 and Class 12 Science Notes, Classification of Elements PDF in Hindi and English
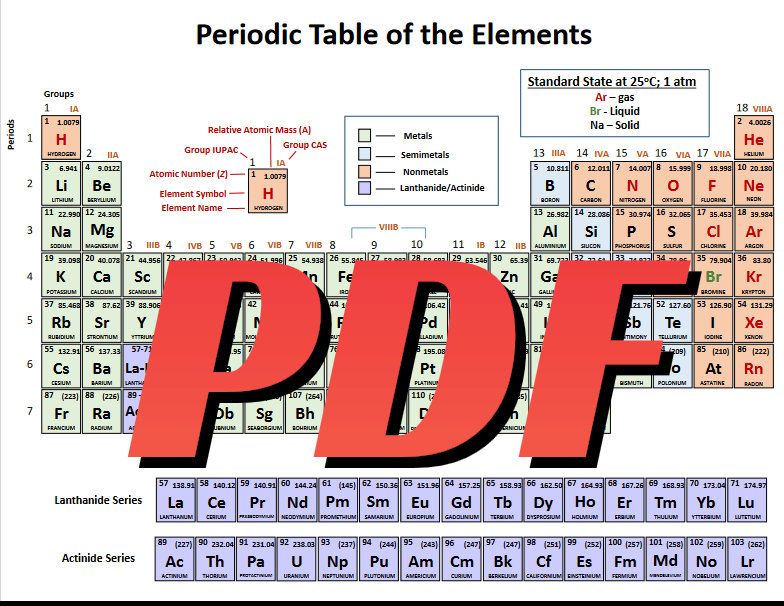
Historical Development of Periodic Table
The journey to the modern-day periodic table began in the early nineteenth century. Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian chemist, is regularly credited with its creation in 1869. Mendeleev organized the 63 acknowledged elements primarily based on their atomic mass and noticed that certain properties recurred periodically. This periodicity enabled him to be expecting the existence and properties of elements that had but to be observed, filling gaps in his table with incredible accuracy.
In the early 20th century, Henry Moseley, an English physicist, refined the desk by organizing elements with the aid of their atomic wide variety as opposed to atomic mass. This reorganization resolved preceding inconsistencies and installed the current periodic regulation: the properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic numbers.
Structure of the Periodic Table
The periodic table is established into rows known as periods and columns called groups or households. Elements are organized in growing order of atomic wide variety, which represents the number of protons in an atom's nucleus. This arrangement exhibits recurring tendencies in elemental residences, which includes electronegativity, ionization power, and atomic radius.
Periods
Each row of the periodic table corresponds to a duration, indicating the wide variety of electron shells in the atoms of the factors inside that row. For example, all factors within the second duration have two electron shells.
Groups:
Columns, or agencies, are numbered from 1 to 18 and categorize factors with comparable chemical and physical residences. For example, Group 1 consists of the alkali metals, that are incredibly reactive, mainly with water. Group 17 homes the halogens, known for their reactivity with metals to shape salts, while Group 18 comprises the noble gases, that are significantly inert due to their whole electron shells.
Blocks:
The desk is likewise divided into blocks primarily based at the electron configuration of the elements: the s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block. This classification displays the subshell in which the "ultimate" electron is living.
Trends inside the Periodic Table
Understanding the periodic developments is critical for predicting and explaining the conduct of factors:
Atomic Radius
Generally decreases throughout a period from left to proper due to increasing nuclear price, which draws electrons towards the nucleus. It will increase down a collection as additional electron shells are delivered.
Ionization Energy: The electricity required to eliminate an electron from an atom. It normally will increase throughout a period and reduces down a group, influenced with the aid of atomic radius and nuclear price.
Also read:
Electronegativity
The tendency of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond. It follows a similar fashion to ionization strength, increasing across periods and reducing down groups.
Applications and Importance
The periodic table's predictive energy extends across chemistry, physics, or even biology. It aids within the discovery of new elements and substances, understanding chemical reactivity, and the development of latest technologies. For example, the semiconductor industry is predicated on elements like silicon and germanium, whose properties are well understood thru their positions inside the periodic table.
In medication, radioactive isotopes used in cancer treatment and diagnostic imaging are decided on based totally on their predictable conduct as deduced from their periodic placement. The periodic table additionally guides environmental technology, in which know-how approximately elemental cycles and interactions enables cope with issues like pollutants and aid management.
Future of the Periodic Table
As clinical knowledge expands, so does the periodic table. The discovery of latest elements, mainly the ones past uranium (atomic range 92), has led to the extension of the table. These super-heavy factors, synthesized in laboratories, assignment our understanding of atomic structure and nuclear stability.
Continued research might also unveil new developments and relationships, potentially leading to the improvement of recent substances with exceptional residences. The periodic desk remains a dynamic and evolving device, fundamental to the advancement of technological know-how.

![[PDF*] Navy MR Complete Study Material Books | Practice Set | Previous Year Paper | Mock Test Free](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEju1OtWAETNykdIMMl1EccY2golN8cIsZ6kuKw89_a63nGAYBg2hGx_cn33HhLBgy8dKG_PM5Kamkr0Iazf2gkEDbCMhornMbFLiHxo33Qu7ToC3cfpjr6X_RFAZym3KmdUhVOKmFtZQ_w/w72-h72-p-k-no-nu/1010.jpg)
0 Comments
Thanks for comment!